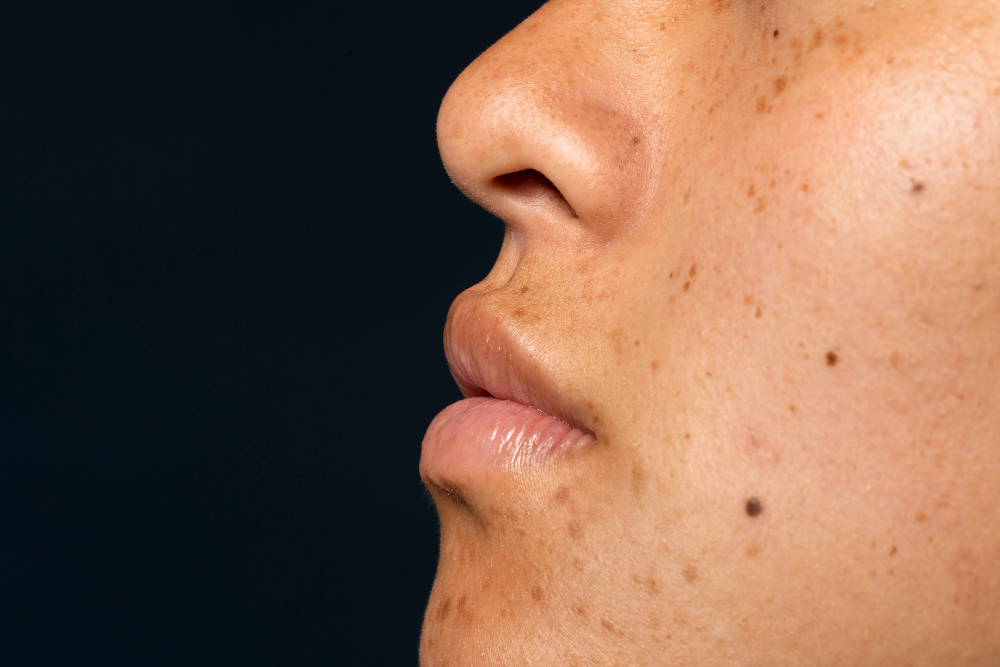
What is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation is the color of your skin. It comes from a natural pigment called melanin. Everyone has melanin, but the amount can vary. Because of this, people have different skin tones. Sometimes, skin pigmentation changes. For example, you may notice dark or light patches. These changes can happen for many reasons. Understanding skin pigmentation helps you care for your skin better.
Common Causes of Skin Pigmentation
Many things can cause changes in skin pigmentation. Some are harmless, while others may need treatment. Knowing the causes of skin pigmentation can help you prevent problems. Here are some common reasons:
In different climates, sun exposure may play a bigger role. For example, people living in sunny areas may notice more changes.
Symptoms and Types of Pigmentation Disorders
Skin pigmentation disorders can look different. You may see spots, patches, or changes in your skin’s color. Here are some common types:
Sometimes, these changes are mild. However, they can also be more noticeable and affect self-confidence.
Diagnosis: How Skin Pigmentation is Identified
Doctors use several ways to diagnose skin pigmentation problems. First, they look at your skin. Then, they may ask about your health history. Sometimes, they use special lights to see the patches better. In rare cases, a small skin sample may be tested. This helps find the exact cause. Early diagnosis can lead to better treatment for skin pigmentation.
Treatment Options for Skin Pigmentation
Treatment for skin pigmentation depends on the cause. Some changes fade on their own. But, other times, you may need help. Here are some common treatments:
Always talk to a dermatologist before starting any treatment. Some products may not be safe for all skin types.
Lifestyle Tips and Prevention
While you cannot prevent all skin pigmentation changes, you can lower your risk. Here are some helpful tips:
With these steps, you can help prevent skin pigmentation problems and keep your skin healthy.
When to See a Dermatologist
Sometimes, skin pigmentation changes need expert care. You should see a dermatologist if:
Early help can prevent problems from getting worse. A dermatologist can suggest the best treatment for your skin pigmentation concerns.
If you have questions or notice changes in your skin, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice on skin pigmentation concerns.